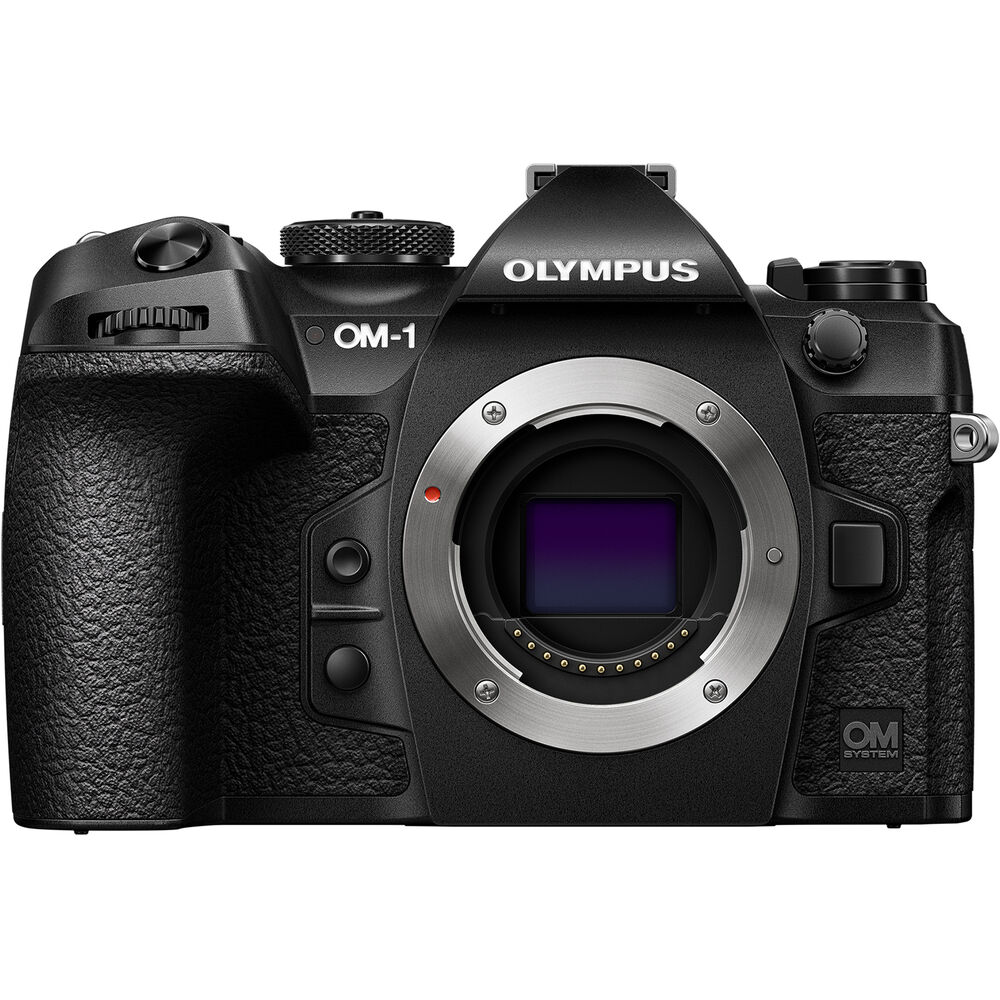
OM-1: B&H Photo / Amazon / Adorama
Last night OM systems announced its latest Olympus camera the Olympus OM-1 with a pretty substantial price tag attached. I am curious to see how the Quad Bayer technology ends up working for noise performance and more, but I think it will be far more useful on APS-C and Full-Frame sensors. Below you can read a summary of what the technology has to offer.
Advantages of Quad Bayer Coding (QBC) – High sensitivity and high resolution in one sensor
The Quad Bayer structure means four adjacent pixels are clustered with the same-color filters. In this way, high sensitivity and high resolution can be achieved in one sensor. It can, for example, prevent resolution loss in a low-illuminance environment and produce low-noise nightscape photos.
How was QBC invented?
Smartphone cameras have been rapidly improving their image quality for the last few years. The high demand for better quality images is driving the trend to miniaturize pixels in the image sensor for smartphones so that more pixels can be crammed in to achieve higher resolutions. However, the miniaturization of pixels comes with a tradeoff: the sensor sensitivity must be compromised.
Addressing this problem, Sony has developed a pixel array which is called QBC. It minimizes the sensitivity loss due to physical size reduction of a pixel. The technology is in a sense specifically developed for smartphone image sensors, for larger sized sensors, such as ones applied in SLR cameras, can accommodate larger pixels and not requiring pixel miniaturization.
- Conventional sensor Bayer structure
- QBC sensor QBC structure(Array of the same color every two pixels)
- Shot by image sensor with Bayer structure
- Shot by image sensor with Quad Bayer structure (IMX689)
What is QBC?
When shooting in an environment of low illuminance, such as nightscapes, adjacent four pixels are clustered to create per-unit image signal that is four times greater than that of a single pixel.
By adding of adjacent pixels in analog, loss of resolution is prevented, enabling to reduce noise in the resulting image. The result is the enhanced sensitivity in low-illuminance environments, enabling low-noise, bright images for photos and movies. Meanwhile, in high-illuminance environments, such as outdoor in daylight, the sensor can revert the pixels to the Bayer structure by advanced processing of array conversion (remosaic) to achieve the high resolution of Bayer sensors.
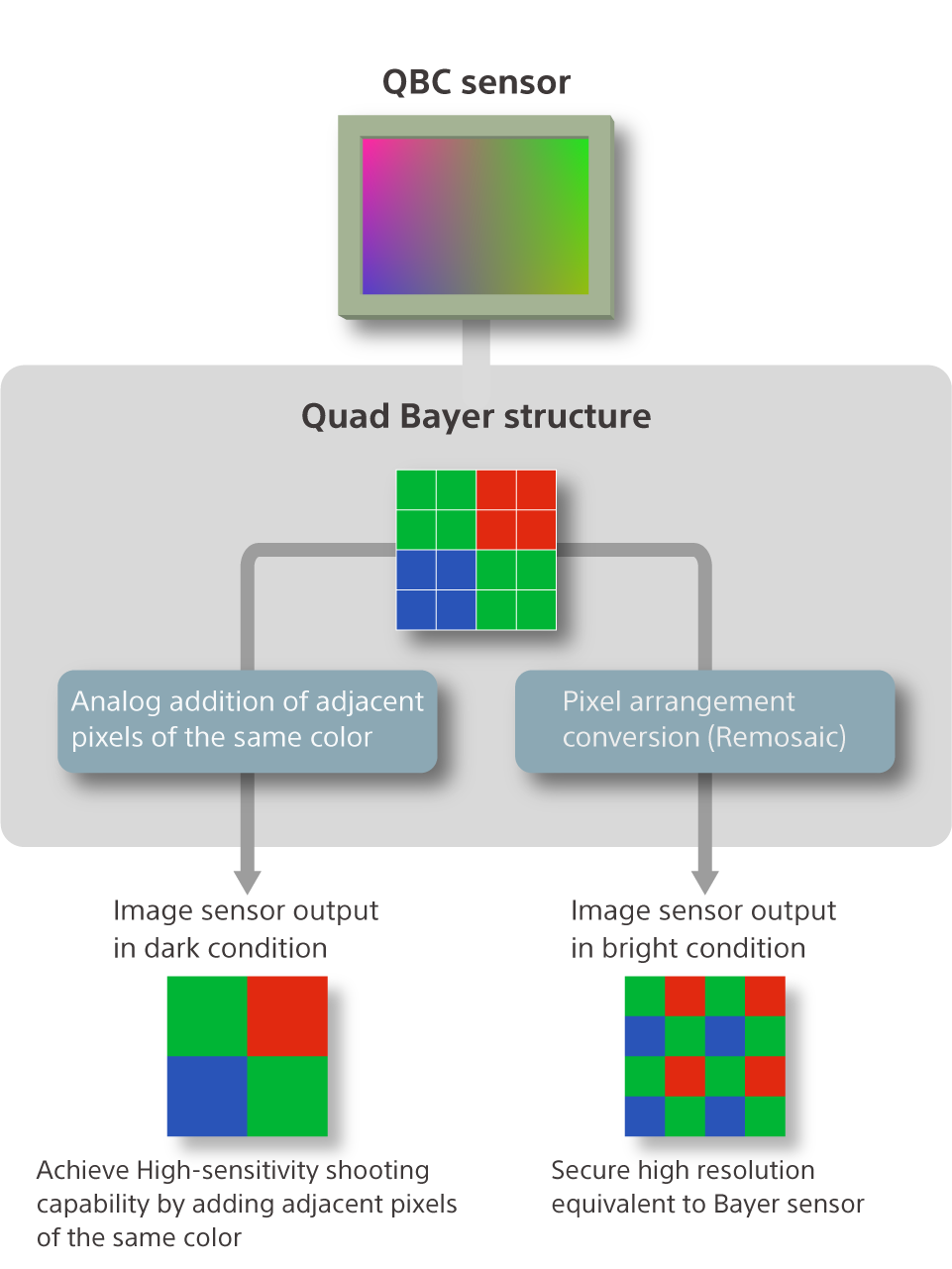
Sony’s original array conversion circuit is integrated into the image sensor chip, which enables processing of array conversion (remosaic) within the sensor as opposed to the conventional software-based conversion. This contributes to low power consumption compared to software processing. The built-in array conversion circuit also enables real-time processing, so it can be leveraged when capturing videos.